Answer to question 1
An increase in CO2 in a modified atmosphere can lead to an increased lag time for many spoilage bacteria which can prolong shelf life. It can also inhibit spoilage moulds.
Answer to question 2
In descending order, with the greatest association with C.botulinum first:
Raw fish, smoked fish, fresh leaf salad, Cooked meat, cheese,
Answer to question 3
A small percentage of Oxygen is often retained within modified atmosphere packages to inhibit the outgrowth of anaerobes. However, residual O2 levels are never considered to be an adequate control to prevent the outgrowth and toxin formation by C.botulinum.
In fresh meat packaging, residual O2 can improve the appearance of the food.
Answer to question 5
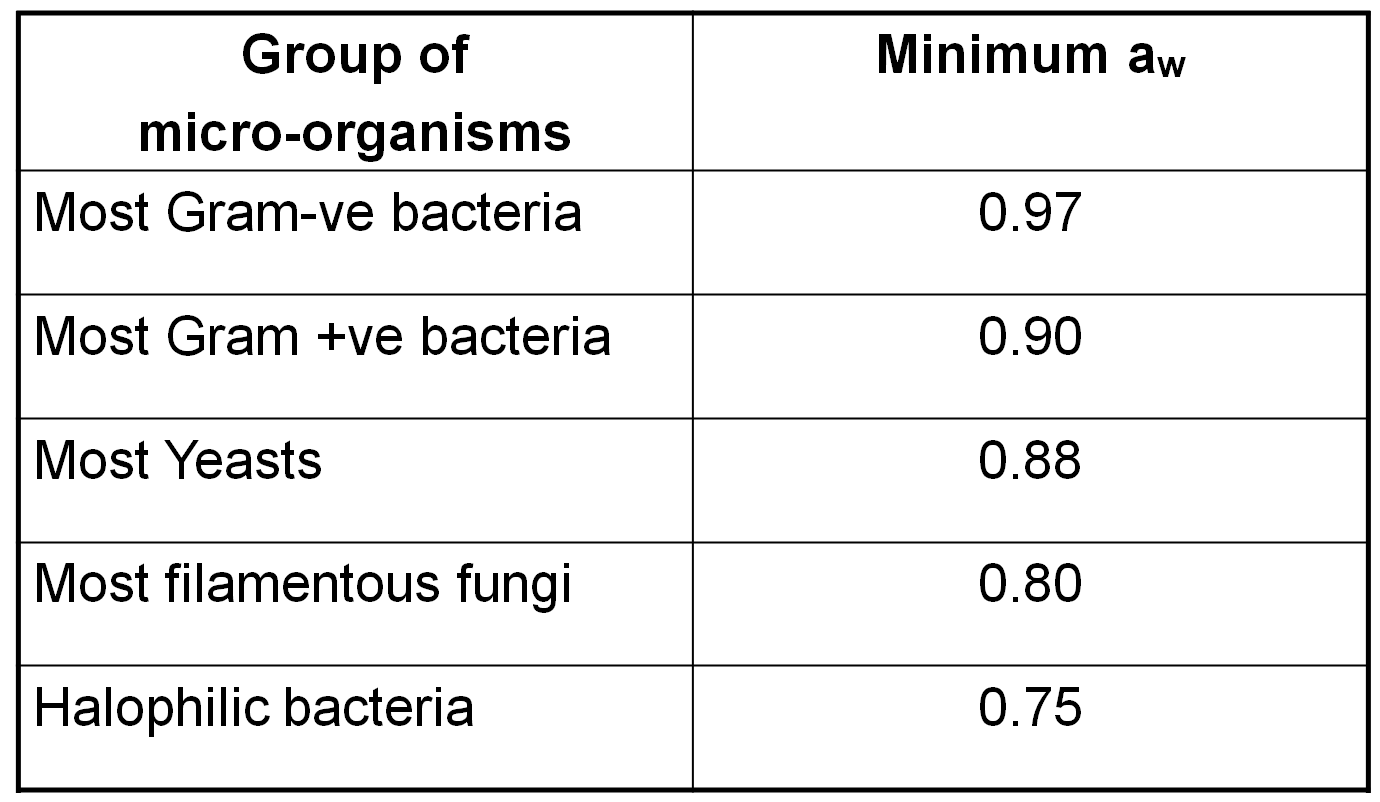
The water activity is a measure of the amount of liquid water available in the food for microbial growth. Pure water will have an aw of 1.0 and the presence of solutes will reduce this figure to <1.0
The water activity of a given food enables the prediction of possible bacterial growth in that food and permits growth restriction parameters to be set.
Bacteria generally require high aw for growth whereas moulds and yeasts are able to grow in dry environments. Some typical water activity limits for growth include:
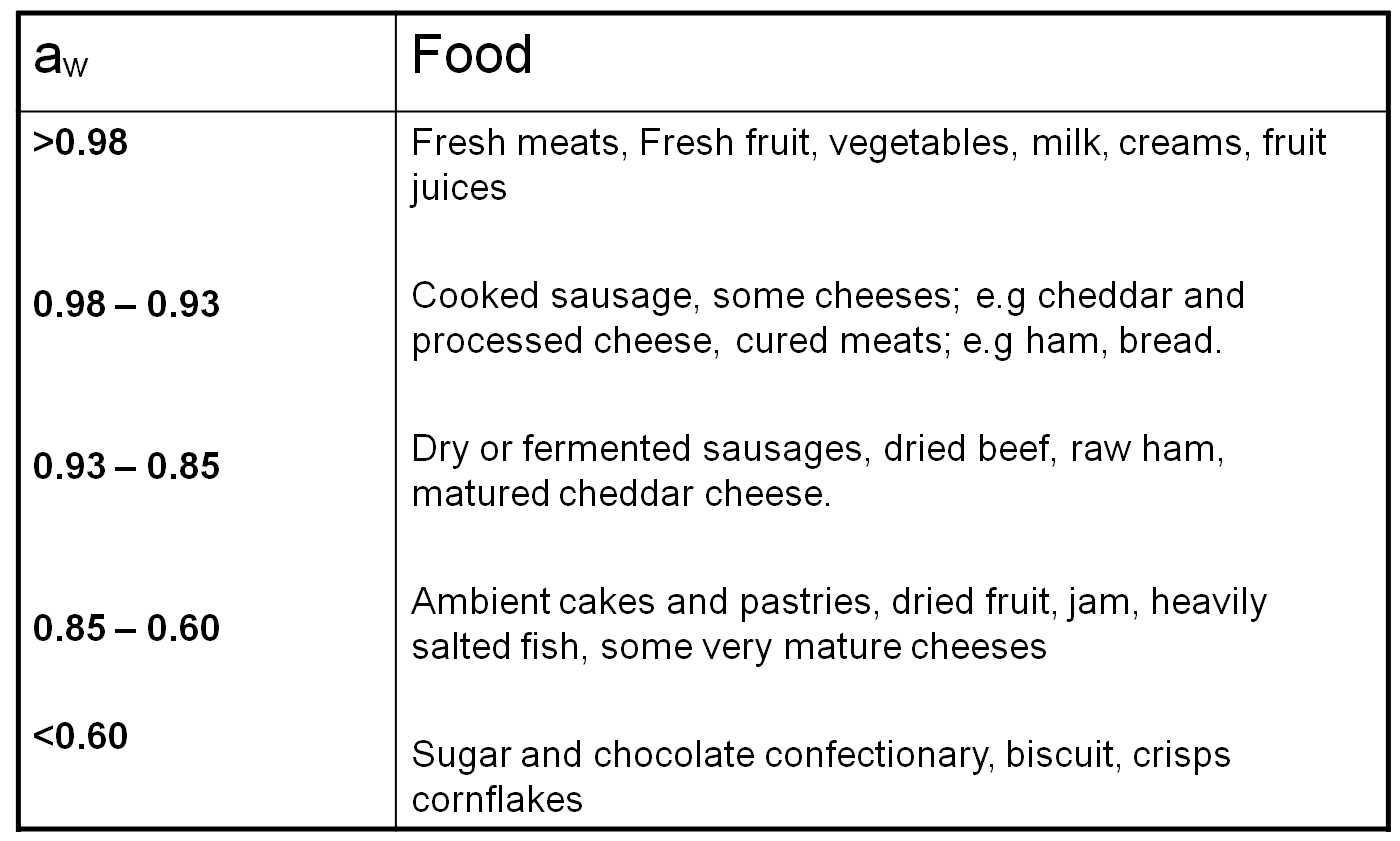
Some typical water activity levels in common foods include:
Answer to question 6
The most significant microbiological hazards associated with this product are C.botulinum and L.monocytogenes. In addition Salmonella spp, E.coli o157 and other aerobic pathogens are also significant.
Answer to question 7
The critical control points for the prevention of C.botulinum outgrowth and toxin production are the brining (salting) of the fish and the storage.
Answer to question 8
The critical limits at these CCPs are:
Brining: 3.5% salt throughout the fish flesh. This might translate to placing the fish into a particular concentration of salt in a water bath for a specified time. The thickness of the fish fillet may also be a critical point for this method.
Storage: Refrigerated storage at between 3°C and 8°C. If less than 3°C can be guaranteed then the brining stage will no longer be a critical control point because C.botulinum is incapable of growth at these temperatures, but this would be very difficult to achieve in practice. If the brining were not carried out effectively the shelf life should be restricted to 10 days at 8°C.
Answer to question 10
The critical limits are 70°C for 2 minutes or equivalent at the core of the fish
Answer to question 11
Monitoring must be carried out at the CCPs to ensure that the critical limits are achieved. Therefore the following should be carried out as a minimum: Monitoring of
- The salt concentration in the brine bath, normally by hydrometer or brinometer
- The fish fillet size
- The product temperature during smoking
- The time of hot smoking
- The storage temperature
Answer to question 12
Where monitoring identified a failure to achieve a critical limit one would expect Fred to:
- Ensure that the food is fully processed by extending the period of brining/smoking as appropriate
- Investigate why there has been a failure and rectify the problem
- Identify any suspect product which may have already been produced and ensure adequately processed or destroyed.
Answer to question 13
Verification should have taken place with respect to the process method. Firstly the method of brining and smoking should be validated, that is, based on an accepted scientific method. Secondly, if the salt content in the water bath is to be monitored, initial verification product trials should have been carried out to demonstrate that the time/brine combinations are adequate to achieve the desired salt content in the fish. Similarly verification checks should demonstrate that the core temperature of the fish during the smoking process always reaches the desired level.
Initial microbiological testing might be helpful with respect to L.monocytogenes but would not be necessary if the critical limits of 70°C for 2 minutes could be guaranteed.
The system should also be periodically reviewed to ensure that it is working effectively.
Answer to question 14
Documentation should be available to demonstrate that the correct CCPs and critical limits have been identified, the methods of monitoring and undertaking corrective actions. Records should be retained for any monitoring, corrective actions and verification activities performed.